Introduction
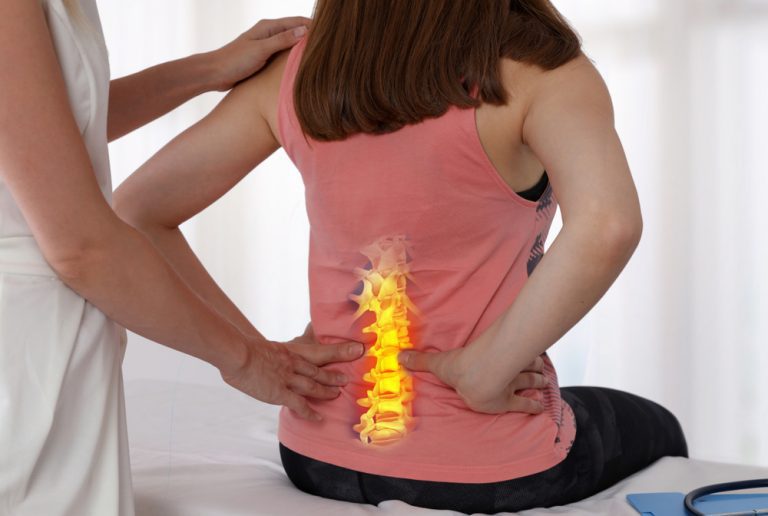
Lower back pain is one of the most common health problem affecting people of all ages and genders. It is one of the most prevalent musculoskeletal pain or disorders worldwide, and it can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. While lower back pain affects both males and females, it is more common in women due to their unique anatomical and physiological characteristics that cause of back pain.
What Causes Lower Back Pain in Females? In this article, we will explore the common causes of low back pain in females, their diagnosis, and treatment options. Understanding the causes of lower back pain in females is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals to effectively manage and prevent this condition.
Anatomy of the Lower Back Spine
The lower back, also known as the lumbar spine, is a complex structure composed of bones, muscles in the back, ligaments, and nerves. The spinal column in the lower back consists of five lumbar vertebrae, which are separated by intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers. The vertebrae are connected by facet joints, which allow for movement and flexibility in the lower back.
The muscles and ligaments in the lower back play a crucial role in supporting the spinal column and maintaining proper posture. The erector spinal muscles run parallel to the spinal column and help to extend the back and maintain an upright posture.
The quadratus lumborum muscles are located on either side of the spine and help to stabilize the lower back during movement. The transverse abdominal muscles, which are part of the core muscles, wrap around the lower abdomen and back, providing stability and support to the lumbar spine.
The ligaments in the lower back connect the vertebrae and provide additional support to the spinal column. The anterior longitudinal ligament runs along the front of the vertebral bodies, while the posterior longitudinal ligament runs along the back of the vertebral bodies.
The ligamentum flavum connects the lamina of adjacent vertebrae and helps to maintain proper alignment of the spine. The interspinous ligaments connect the spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae and help to limit excessive flexion of the spine.
Together, these components of the lower back work in harmony to provide support, stability, and flexibility to the spine, enabling movement and preventing injury.
What Causes Upper Back Pain in Females
Upper back pain can happen to females for various reasons, such as poor posture, muscle strain or injury, and underlying medical conditions like osteoporosis or fibromyalgia. Poor posture occurs due to long hours of sitting or carrying heavy bags, which strains the muscles and joints in the upper back. Muscle strain or injury can also occur from lifting heavy objects or playing contact sports. Osteoporosis and fibromyalgia, which are medical conditions that weaken bones or cause chronic pain, can also cause upper back pain. Stress, anxiety, and depression can make the pain worse. To treat upper back pain, one can consider physical therapy, chiropractic care, medication, or surgery in severe cases. Maintaining good posture, regular exercise, and stress-management techniques can also prevent upper back pain in females.
What Causes Lower Back Pain in Females?
Pregnancy and childbirth
What can cause lower back pain in a woman pregnant? Pregnancy and childbirth are common causes of back pain in females. During pregnancy, hormonal changes cause the ligaments and joints pain in pelvis and lower back female to relax, which can lead to instability and pain.
As the uterus grows, the weight of the fetus shifts the center of gravity forward, placing additional stress on the chronic low back pain. In some cases, the growing uterus can compress the sciatic nerve, leading to sciatica, a type of pain that radiates from the lower back down to the legs.
During childbirth, the muscles and ligaments in the lower back are put under significant strain, which can cause pain and discomfort. Women who have undergone a cesarean section may experience lower back pain due to the incision and scar tissue formation.
In some cases, women may develop a condition known as diastasis recti, in which the abdominal muscles separate during pregnancy, leading to a weakened core and increased strain on the lower back.
Menstrual Cycle and Hormonal Changes
The menstrual cycle and hormonal changes can also contribute to lower back pain causes in females. The release of prostaglandins during menstruation can cause the muscles pain in the uterus to contract, leading to cramping and pain.
These contractions can also affect the muscles in the lower back, leading to pain and discomfort. Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can also lead to water retention and bloating, which can place additional pressure on the lower back.
In some cases, hormonal changes related to menopause can also contributing pain in the lower back. As estrogen levels decline, the bones and muscles in the body can weaken, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
This can lead to compression fractures in the vertebrae of the lower spine, causing lower back pain. Hormonal changes can also affect the joints and ligaments in the lower back, leading to instability and pain.
Pelvic Organ Conditions, Such as Endometriosis and Uterine Fibroids
Pelvic organ conditions such as endometriosis and uterine fibroids can also cause lower back pain in females. Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing inflammation and pain. This inflammation can affect the muscles and ligaments in the lower back, leading to what causes lower back pain in females left side and what causes lower back pain in females right side and makes irritations, discomfort in regular life.
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. As they grow, they can place pressure on the surrounding organs, including the lower back. This pressure can cause pain and discomfort in the lower back, as well as other symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, abdominal pain, and urinary frequency.
Other pelvic conditions, such as ovarian cysts and pelvic inflammatory disease, can also cause back pain in females. These conditions can cause inflammation and swelling in the pelvic region, which can affect the muscles and ligaments in the lower back, leading to back pain and discomfort.
Osteoporosis Causes and Other Bone Disorders
Osteoporosis and other bone disorders are conditions that can cause lower back pain in females. Osteoporosis is a condition in which the bones become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures. As the bones in the spine become weaker, they can collapse and compress the nerves in the spinal cord, leading to lower back pain.
Other bone disorders that can cause lower back pain include osteoarthritis and degenerative disc disease. Osteoarthritis is a condition in which the cartilage that cushions the joints wears away, causing the bones to rub against each other and leading to pain and stiffness. Degenerative disc disease is a condition in which the discs between the vertebrae of the spine break down, leading to pain and inflammation.
These bone disorders can also affect the alignment of the spine, causing it to curve and leading to lower back pain. In addition, they can lead to the development of spinal stenosis, a condition in which the spinal canal narrows and puts pressure on the nerves, leading to pain and discomfort.
Treatment for lower back pain caused by bone disorders may include pain management, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery to address the underlying condition. In addition, lifestyle modifications such as exercise and a healthy diet can help to strengthen bones and improve overall bone health.
Muscular Strains and Sprains
Muscular strains and sprains are common causes of lower back pain in females. Strains occur when the muscles or tendons in the lower back are stretched or torn, while sprains occur when the ligaments that hold the bones together are stretched or torn. These injuries can be caused by overuse, improper lifting techniques, or sudden movements that place excessive stress on the muscles and ligaments in the lower back.
Symptoms of muscular strains and sprains may include pain and stiffness in the lower back, as well as muscle spasms and difficulty moving. These injuries can also cause swelling and inflammation in the affected area.
Treatment for muscular strains and sprains may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce swelling and inflammation, as well as pain medication and muscle relaxants to alleviate pain and muscle spasms. Physical therapy may also be recommended to help strengthen the muscles in the lower back and improve flexibility and range of motion.
Prevention of muscular strains and sprains can be achieved through proper lifting techniques, maintaining good posture, and regular exercise to strengthen the muscles in the lower back. It is also important to avoid sitting for long periods of time and to take frequent breaks to stretch and move around.
Posture and Body Mechanics
Poor posture and body mechanics can also contribute to lower back pain in females. Sitting or standing with improper posture can put additional stress on the muscles and ligaments in the lower back, leading to pain and discomfort.
Sitting for prolonged periods of time can also contribute to lower back pain, particularly if the chair does not provide proper support for the lower back. Similarly, standing for long periods of time, particularly in high heels or without proper footwear, can place additional stress on the lower back muscles and ligaments.
Improper lifting techniques can also cause lower back pain. Lifting heavy objects with the back muscles instead of the legs can put excessive strain on the lower back, leading to muscle strains and sprains.
Treatment for lower back pain caused by poor posture and body mechanics may include physical therapy to improve posture and strengthen the muscles in the lower back. In addition, lifestyle modifications such as incorporating regular exercise, maintaining proper posture, and taking frequent breaks to stretch and move around can help to alleviate lower back pain caused by poor posture and body mechanics.
Prevention of lower back pain caused by poor posture and body mechanics involves maintaining good posture while sitting and standing, using ergonomic chairs and other equipment, wearing supportive footwear, and using proper lifting techniques. Stretching and strengthening exercises can also be beneficial in maintaining good posture and reducing the risk of lower back pain.
Obesity and Weight Gain
Obesity and weight gain can also contribute to lower back pain in females. Excess weight places additional stress on the lower back muscles and ligaments, leading to pain and discomfort. In addition, carrying excess weight in the abdominal area can cause an imbalance in the body’s center of gravity, further increasing the strain on the lower back.
Furthermore, obesity is also linked to other conditions that can cause lower back pain, such as osteoarthritis and degenerative disc disease. These conditions can be exacerbated by excess weight, making it more difficult to manage lower back pain.
Treatment for lower back pain caused by obesity and weight gain may include weight loss through diet and exercise to reduce the strain on the lower back muscles and ligaments. In addition, physical therapy may be recommended to help strengthen the muscles in the lower back and improve flexibility and range of motion.
Prevention of lower back pain caused by obesity and weight gain involves maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. This can help to reduce the strain on the lower back muscles and ligaments, as well as prevent the development of other conditions that can cause lower back pain.

Diagnosing Lower Back Pain in Women
What Causes Lower Back Pain in Females. Diagnosing the underlying cause of lower back pain in females involves a comprehensive medical evaluation. The following are some common methods used by healthcare professionals to diagnose lower back pain:
Physical Examination and Medical History: A healthcare provider will typically conduct a physical examination and take a detailed medical history to assess the nature and severity of the pain, as well as any other symptoms or risk factors that may be contributing to the pain.
Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, can be used to visualize the structures of the lower back, including the bones, muscles, and ligaments. These tests can help identify structural abnormalities or damage that may be causing the pain.
Blood Tests: Blood tests may be used to rule out underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to lower back pain, such as infections, autoimmune disorders, or metabolic conditions.
Other diagnostic tests may include nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG) to assess nerve function and muscle activity in the lower back.
It is important to note that lower back pain is often a complex and multifaceted condition, and diagnosing the underlying cause may require a combination of different diagnostic methods. A thorough medical evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential to accurately diagnose and treat lower back pain in females.
Treatment Options for Lower Back Pain in Females
Treatment options for lower back pain in females may vary depending on the underlying cause of the pain. Some common treatment options include:
Pain Management Strategies: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen, may be used to relieve mild to moderate lower back pain. In more severe cases, prescription medications, such as muscle relaxants, opioid painkillers, or corticosteroids, may be recommended.
However, these medications should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider due to potential side effects and the risk of addiction.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Exercises: Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles in the lower back and improve flexibility and range of motion. Rehabilitation exercises, such as stretches and strengthening exercises, may also be recommended to help reduce pain and improve overall function.
Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle modifications can be helpful in managing and preventing lower back pain. These may include maintaining good posture, using ergonomic chairs and other equipment, wearing supportive footwear, using proper lifting techniques, and taking frequent breaks to stretch and move around. Weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise can also be beneficial in reducing the strain on the lower back muscles and ligaments.
Other treatment options for lower back pain may include chiropractic care, acupuncture, massage therapy, and other complementary and alternative therapies. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any new treatments, as some therapies may not be effective or may even be harmful.
Prevention of Lower Back Pain for Affected Woman
Prevention of lower back pain in females is an important goal, as it can help avoid the development of chronic lower back pain and related disability. Some effective strategies for preventing low back pain in women include
Exercise and Stretching Routines: Regular exercise and stretching can help strengthen the muscles in the lower back and improve flexibility and range of motion. Activities such as yoga, Pilates, and tai chi can be particularly effective in promoting core strength and reducing lower back pain.
Maintaining Proper Posture and Body Mechanics: Proper posture and body mechanics can help reduce strain on the lower back muscles and ligaments. This includes sitting with proper back support, avoiding slouching or hunching over, and using proper lifting techniques.
Weight Management and Healthy Diet: Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce the strain on the lower back muscles and ligaments. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains can also help promote overall health and reduce inflammation, which can contribute to back pain.
Avoiding High-Impact Activities or Movements that Strain the Lower Back: Activities such as heavy lifting, high-impact exercise, and repetitive motions that strain the lower back should be avoided or performed with caution. This includes activities such as running, jumping, and lifting heavy weights, which can put significant stress on the lower back muscles and ligaments.
Overall, what causes lower back pain in females involves a multifaceted approach, including regular exercise, maintaining proper posture and body mechanics, weight management, and avoiding high-impact activities or movements that strain the lower back. By adopting these strategies, females can reduce their risk of developing lower back pain and improve their overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Lower back pain is a common and often debilitating condition that can affect females of all ages. Understanding the common causes of lower back pain in females is important in order to develop effective treatment and prevention strategies.
While there are many potential causes of lower back pain in females, including pregnancy and childbirth, hormonal changes, pelvic organ conditions, osteoporosis and other bone disorders, muscular strains and sprains, posture and body mechanics, and obesity and weight gain, there are also many treatment and prevention strategies that can be employed to reduce pain and improve function.
These may include pain management strategies, physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises, lifestyle modifications, and other complementary and alternative therapies. By adopting a multifaceted approach to the management and prevention of lower back pain in females, it is possible to improve quality of life and reduce the risk of chronic pain and disability. In this article, we have discussed about what causes lower back pain in females.
Written by.
Dr. Saiful Islam, PT
BPTh (DU), MPTh (Orthopedics) – NIPS, India
PG Certificate in Acupuncture, India
Specially trained in Ozone Therapy, USA and Ozone Forum, India.
Physiotherapy Consultant, Vision Physiotherapy Center.
To consult: 01760-636324 , 01932-797229 (9:00 AM to 9:00 PM) and make an appointment.
Our Facebook page: Vision Physiotherapy Center